How To Change Laptop Processor – Best Complet Guide
How to Successfully Change Your Laptop Processor
Change Laptop Processor can be a daunting task, but it can also be a cost-effective way to improve the performance of an aging laptop. Understanding the components of a laptop and the compatibility of processors is crucial before attempting to change a processor. In this article, we will provide step-by-step instructions on how to change a laptop processor and provide tips on how to choose the right processor upgrade.

The first step in changing a laptop processor is to identify the current processor and determine the compatibility of potential upgrades. It is important to note that not all laptops are designed to have their processors upgraded. In some cases, the processor may be soldered onto the motherboard, making it nearly impossible to replace. However, for laptops with upgradeable processors, it is important to ensure that the new processor is compatible with the laptop’s motherboard and other components.
Once the compatibility of the new processor is confirmed, the laptop must be disassembled to access the processor. This process requires a steady hand and careful attention to detail to avoid damaging the delicate components of the laptop. After removing the old processor, the new processor can be installed, and the laptop can be reassembled. Finally, it is important to test the new processor to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding laptop processors and compatibility is crucial before attempting to change a processor.
- Careful disassembly and reassembly of the laptop is required to avoid damage to delicate components.
- Testing the new processor is essential to ensure proper functionality.
Understanding Laptop Processors

A laptop’s processor, or CPU, is the brain of the computer. It is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. The CPU’s performance can greatly affect the overall performance of the laptop.
There are two main manufacturers of laptop processors: Intel and AMD. Intel processors are generally considered to be more powerful and efficient, while AMD processors are typically less expensive. However, AMD has made significant strides in recent years and now offers some processors that can compete with Intel’s top offerings.
Laptop processors come in different models, each with its own set of specifications. The most important specifications to consider when choosing a laptop processor are:
- Clock speed: This is the speed at which the processor can execute instructions. It is measured in gigahertz (GHz). Higher clock speeds generally mean better performance, but they also consume more power and generate more heat.
- Number of cores: A processor with multiple cores can perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Most laptop processors have two or four cores, but some high-end models have six or eight.
- Cache size: The processor’s cache is a small amount of memory that it uses to store frequently accessed data. A larger cache can improve performance, especially for tasks that require a lot of data processing.
- Thermal design power (TDP): This is the amount of power the processor consumes and the amount of heat it generates. Higher TDPs generally mean better performance, but they also require more power and generate more heat.
It is important to choose a laptop processor that is appropriate for your needs. If you only use your laptop for basic tasks like web browsing and word processing, a lower-end processor may be sufficient. However, if you use your laptop for tasks like video editing or gaming, you will need a more powerful processor.
When upgrading a laptop’s processor, it is important to ensure compatibility between the new processor and the laptop’s motherboard. In many cases, laptop processors are soldered onto the motherboard and cannot be replaced. If the processor can be replaced, it may require disassembling the laptop and removing other components first.
It is also important to note that upgrading a laptop’s processor is not always the most cost-effective way to improve its performance. Upgrading the RAM or storage may provide more noticeable performance improvements for less money.
The Importance of Processor Compatibility
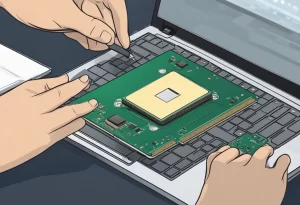
Upgrading a laptop processor requires careful consideration of compatibility with the motherboard, as many processors are soldered on and cannot be replaced independently. Researching compatibility is essential to avoid issues like system instability and overheating, which can occur if the processor’s thermal design power (TDP) exceeds what the motherboard can handle. Additionally, upgrading requires technical expertise and appropriate tools; without them, you risk damaging the laptop’s hardware.
Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a professional technician or the laptop manufacturer before attempting to upgrade the processor. They can provide valuable advice on the compatibility of the processor with the laptop’s motherboard and guide you through the process of upgrading the processor safely and effectively.

Identifying Your Laptop’s Processor
Before upgrading your laptop’s processor, it’s important to identify what processor is currently installed. This will help you determine if an upgrade is possible and what type of processor is compatible.
There are several ways to identify your laptop’s processor:
1. Task Manager
One quick way to check your processor is through the Task Manager. To access the Task Manager, right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” or press Ctrl+Shift+Esc. Click on the “Performance” tab and select “CPU.” The name and speed of your laptop’s CPU will be displayed.
2. System Information
Another way to check your laptop’s processor is through the System Information. To access the System Information, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box, type “msinfo32” and press Enter. In the System Information window, expand the “Components” category and select “Processor.” The name and speed of your laptop’s CPU will be displayed.
3. Manufacturer’s Website
If you know the manufacturer and model of your laptop, you can also check the manufacturer’s website for the specifications of your laptop’s processor. Look for the “Processor” or “CPU” section to find the name and speed of your laptop’s processor.
Once you have identified your laptop’s processor, you can determine if an upgrade is possible and what type of processor is compatible. Keep in mind that not all laptops are upgradeable and compatibility can vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
Choosing the Right Processor Upgrade
When upgrading a laptop’s processor, it’s important to choose the right one for your needs. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a new processor:
Consider the Generation
The generation of a processor can have a significant impact on its performance. Newer generations of processors often have faster speeds, better power efficiency, and improved features. When choosing a processor, it’s important to consider the generation and choose the latest one that is compatible with your laptop.
Check the Processor’s Speed
The speed of a processor is measured in gigahertz (GHz) and determines how quickly it can perform tasks. A higher speed generally means better performance, but it’s important to consider other factors such as the number of cores and the generation of the processor. When choosing a processor, look for one with a speed that meets your needs.
Look at the Number of Cores
The number of cores in a processor determines how many tasks it can perform simultaneously. A processor with more cores can handle more tasks at once, which can improve performance in certain applications. When choosing a processor, consider the number of cores and choose one that meets your needs.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right processor upgrade for your laptop and improve its performance.
How to Safely Disassemble Your Laptop
When it comes to replacing a laptop processor, the first step is to disassemble the laptop. This process can seem intimidating, but with the right tools and techniques, it can be done safely and easily.
Gathering the Necessary Tools
Before beginning the disassembly process, it is important to gather all the necessary tools. These include a small Phillips-head screwdriver and possibly a flathead screwdriver, depending on the make of your laptop. To avoid the possibility of static electricity, it is recommended to wear an ESD wristband, or touch an unpainted piece of metal to discharge any built-up static electricity.
Removing the Laptop Battery
The first step in disassembling a laptop is to remove the battery. This is usually located on the bottom of the laptop and can be removed by sliding the battery release latch and pulling the battery out of the laptop.
Opening the Laptop Case
After the battery has been removed, the next step is to open the laptop case. This can be done by removing any screws that are holding the case together. These screws are usually located on the bottom of the laptop, but can also be found on the sides and back of the laptop.
Once all the screws have been removed, gently pry the case apart using a plastic pry tool or a flathead screwdriver. Be careful not to damage any of the internal components or the case itself.
By following these steps, you can safely disassemble your laptop and begin the process of replacing the processor. Remember to take your time and be patient, as rushing the process can lead to damage to your laptop.
Removing the Old Processor
Before installing a new processor, it is necessary to remove the old one. This section will guide you through the process of removing the old processor.
Locating the Processor
The processor is usually located underneath a heat sink and fan assembly. In some laptops, it may be located under a cover or a metal plate. Refer to the laptop manual or manufacturer’s website to locate the processor.
Unplugging the Processor
Before removing the processor, it is important to unplug it from the motherboard. This can be done by gently lifting the lever or latch that holds the processor in place. Be careful not to damage any of the pins or connectors on the processor.
Lifting the Processor Out
Once the processor is unplugged, it can be lifted out of the socket. Use a gentle twisting motion to loosen the processor from the thermal paste that may be holding it in place. Be careful not to bend any of the pins on the processor.
After the processor has been removed, it is important to clean the old thermal paste from both the processor and the heat sink. This can be done using isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth.
By following these steps, the old processor can be safely and easily removed, making way for a new one to be installed.
Installing the New Processor
Before installing the new processor, it is important to ensure that it is compatible with the laptop’s motherboard. Once compatibility is confirmed, follow the steps below to install the new processor.
Positioning the New Processor
- Begin by carefully removing the old processor from the motherboard. This can usually be done by gently lifting the lever that holds the processor in place.
- Once the old processor is removed, carefully position the new processor in the socket. It is important to align the notches on the processor with the notches on the socket to ensure proper alignment.
- Gently lower the lever to secure the new processor in place. Be sure to apply even pressure to ensure that the processor is properly seated in the socket.
Securing the Processor
- Once the new processor is properly positioned in the socket, it is important to secure it in place. This can usually be done by tightening the screws that hold the processor in place.
- Be sure to refer to the laptop’s documentation to determine the appropriate torque for the screws. Over-tightening the screws can cause damage to the processor or the motherboard.
Reconnecting the Processor
- After the new processor is secured in place, it is important to reconnect any cables or connectors that were removed during the installation process.
- Be sure to refer to the laptop’s documentation to ensure that all cables and connectors are properly connected.
By following these steps, the new processor should be successfully installed and ready for use.
Reassembling Your Laptop
After successfully inserting the new CPU, it’s time to reassemble your laptop. This section will guide you through the process of reassembling your laptop with the new CPU in place.
Closing the Laptop Case
The first step is to put the laptop case back together. Follow these steps:
- Align the bottom cover with the laptop base and snap it into place.
- Use the screws you removed earlier to secure the bottom cover to the laptop base.
- Close the laptop lid and turn it over.
Reinserting the Laptop Battery
Now that the laptop case is closed, it’s time to reinsert the battery. Follow these steps:
- Locate the battery compartment on the bottom of the laptop.
- Slide the battery into the compartment, making sure it is properly aligned.
- Push down on the battery until it clicks into place.
Once the battery is in place, you can power on your laptop and check to make sure everything is working properly. If you encounter any issues, double-check your work to ensure everything is properly reassembled.
That’s it! You’ve successfully changed your laptop processor.
Testing Your New Processor
After successfully installing the new processor, it is important to test it to ensure that it is functioning properly. Here are a few steps to test your new processor:
- Boot the System: Turn on the computer and observe if the system boots up properly. If the system does not boot up, then there may be a problem with the installation process or the compatibility of the new processor with the motherboard.
- Check the BIOS Settings: Access the BIOS settings and check if the new processor is recognized by the system. If the processor is not recognized, then there may be a compatibility issue or the processor may not be installed correctly.
- Benchmarking Software: Use benchmarking software to test the performance of the new processor. This will provide an idea of the processor’s performance compared to the old one. Some popular benchmarking software includes CPU-Z, Geekbench, and Cinebench.
- Stress Testing: Stress testing is important to check the stability of the new processor. This involves running the processor at maximum capacity for an extended period of time to check if it can handle the load without crashing or overheating. Prime95 is a popular stress testing software that can be used for this purpose.
- Temperature Monitoring: It is important to monitor the temperature of the new processor during stress testing to ensure that it does not overheat. Excessive heat can damage the processor and cause it to fail. Software such as HWMonitor can be used to monitor the temperature of the processor.
By following these steps, one can ensure that the new processor is functioning properly and is compatible with the system.
FAQs Of How To Change Laptop Processor?
How can I upgrade the processor in my Dell laptop?
Upgrading the processor in a Dell laptop is possible, but it depends on the specific model. Some Dell laptops have processors that are soldered onto the motherboard, which makes upgrading impossible. However, if the processor is socketed, it can be upgraded. To determine if the processor in your Dell laptop can be upgraded, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact Dell’s customer support.
Is it possible to change the processor of an Acer laptop?
Like Dell laptops, some Acer laptops have processors that are soldered onto the motherboard, which makes upgrading impossible. However, if the processor is socketed, it can be upgraded. To determine if the processor in your Acer laptop can be upgraded, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact Acer’s customer support.
Can I upgrade my laptop processor from Celeron to i3?
It is possible to upgrade a laptop processor from Celeron to i3, but it depends on the specific laptop. The new processor must be compatible with the motherboard and chipset of the laptop. Additionally, the laptop’s cooling system must be able to handle the increased heat generated by the new processor. Before upgrading, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact the manufacturer’s customer support.
Can I upgrade my laptop processor from Pentium to i5?
It is possible to upgrade a laptop processor from Pentium to i5, but it depends on the specific laptop. The new processor must be compatible with the motherboard and chipset of the laptop. Additionally, the laptop’s cooling system must be able to handle the increased heat generated by the new processor. Before upgrading, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact the manufacturer’s customer support.
Can I upgrade my laptop processor from i5 to i7?
It is possible to upgrade a laptop processor from i5 to i7, but it depends on the specific laptop. The new processor must be compatible with the motherboard and chipset of the laptop. Additionally, the laptop’s cooling system must be able to handle the increased heat generated by the new processor. Before upgrading, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact the manufacturer’s customer support.
Can I upgrade my laptop processor from i7 to i9?
It is possible to upgrade a laptop processor from i7 to i9, but it depends on the specific laptop. The new processor must be compatible with the motherboard and chipset of the laptop. Additionally, the laptop’s cooling system must be able to handle the increased heat generated by the new processor. Before upgrading, you should consult the laptop’s manual or contact the manufacturer’s customer support.

I am a technology Specialized writer and blogger based in the USA & UK. I have four years of experience in Cyber Security, Technology, Social Media and all types of electronic devices like computer laptops etc. So I work on solving these issues and give various tips on these issues